Create a Data Pool with sample data
Query the data
Create a Propel Application and get the API credentials
Run the Propel Next.js Starter App
Prerequisites
- Node.js 18.17 or later.
1
Create a Propel Account
Go to the sign-up page, enter your email, password, and click “Get Started”.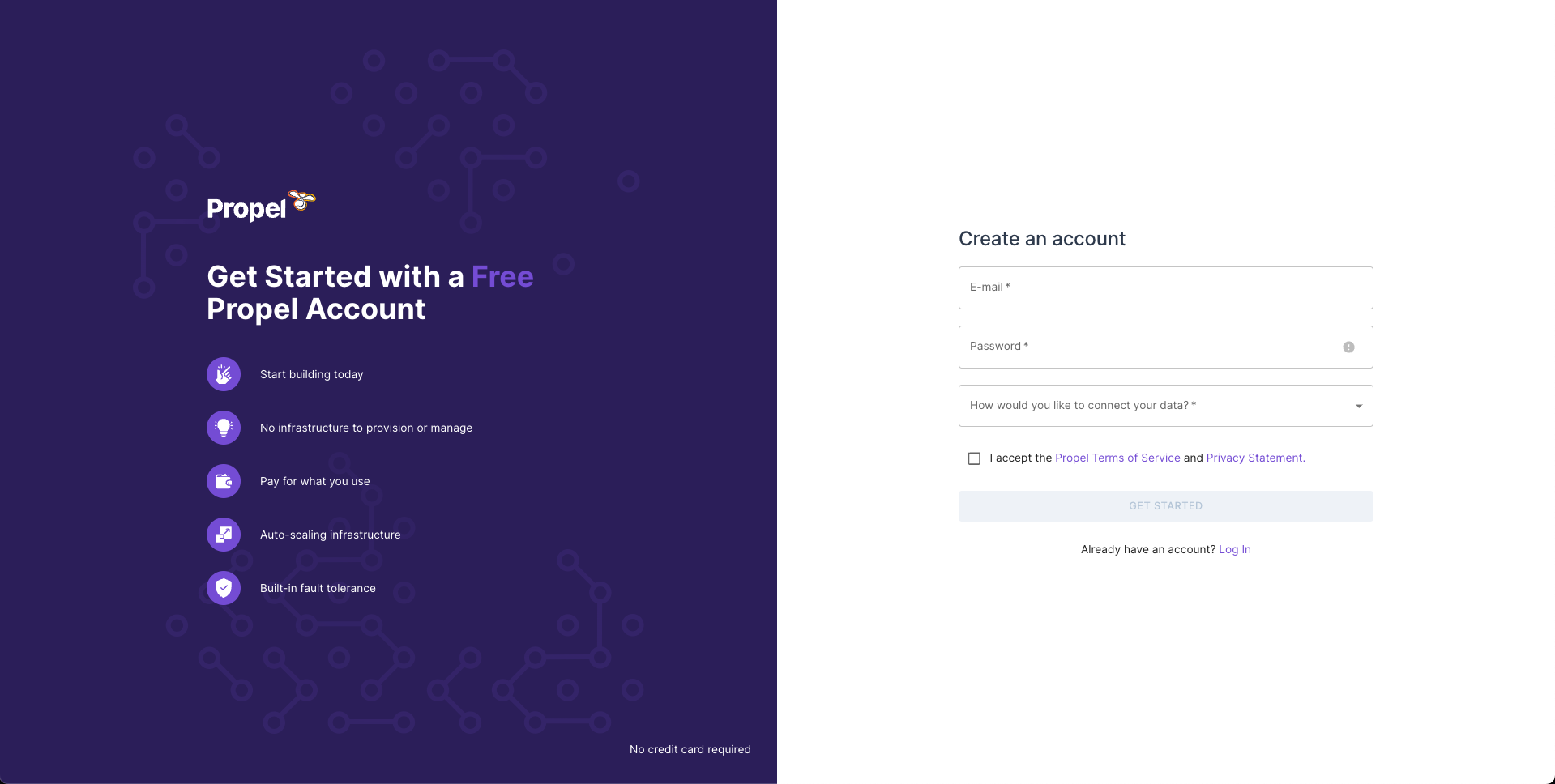
 Confirm your email and log in again.
Confirm your email and log in again. Once you log in, your account will be created, and you will land in the Propel Console.
Once you log in, your account will be created, and you will land in the Propel Console.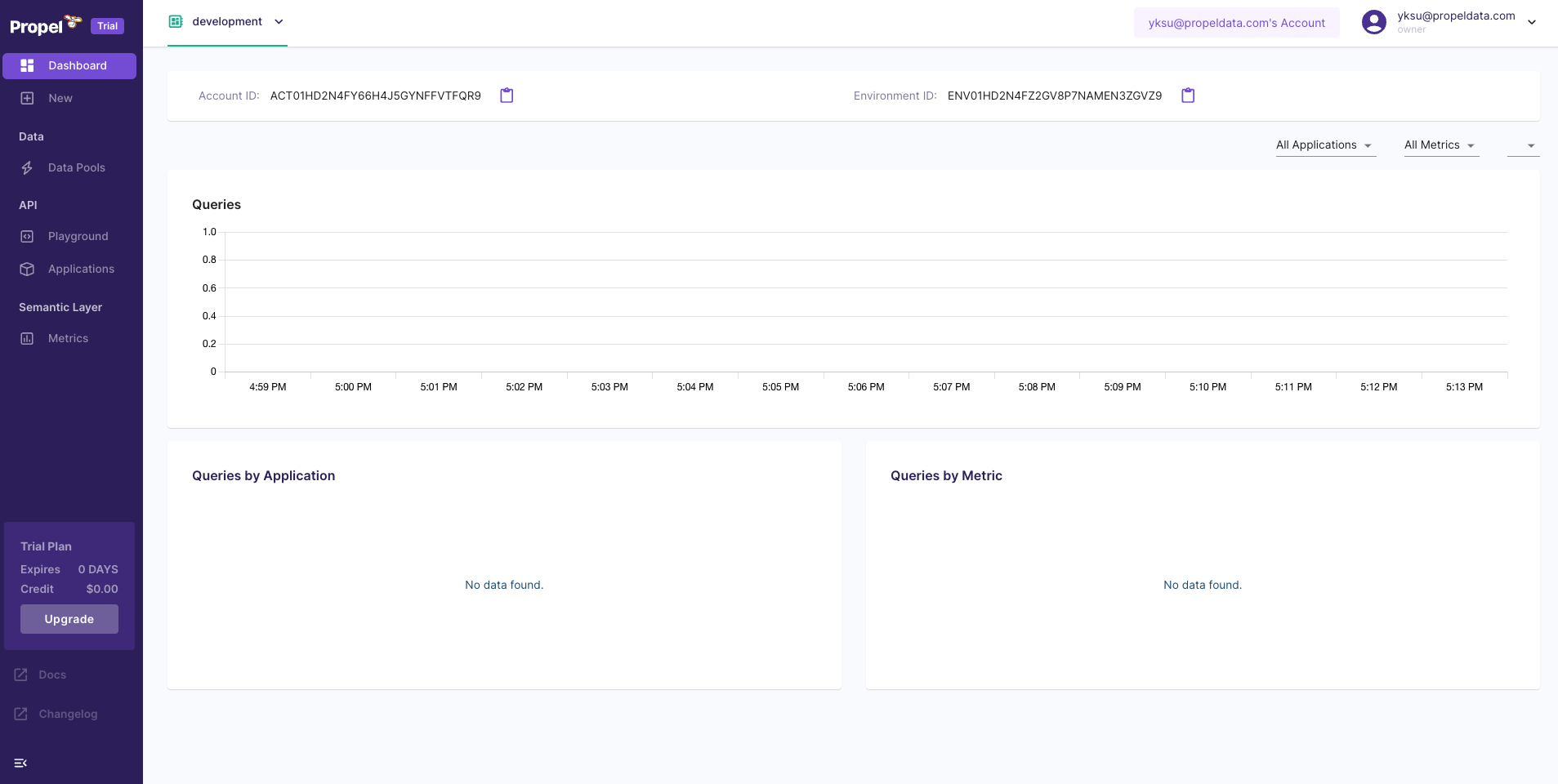




2
Create a Data Pool with sample data
Next, we need some sample data to work with.We’ll need to create a Data Pool. Data Pools are ClickHouse tables that ingest from a data source.Go to “Data Pools”, then click “Create Data Pool”.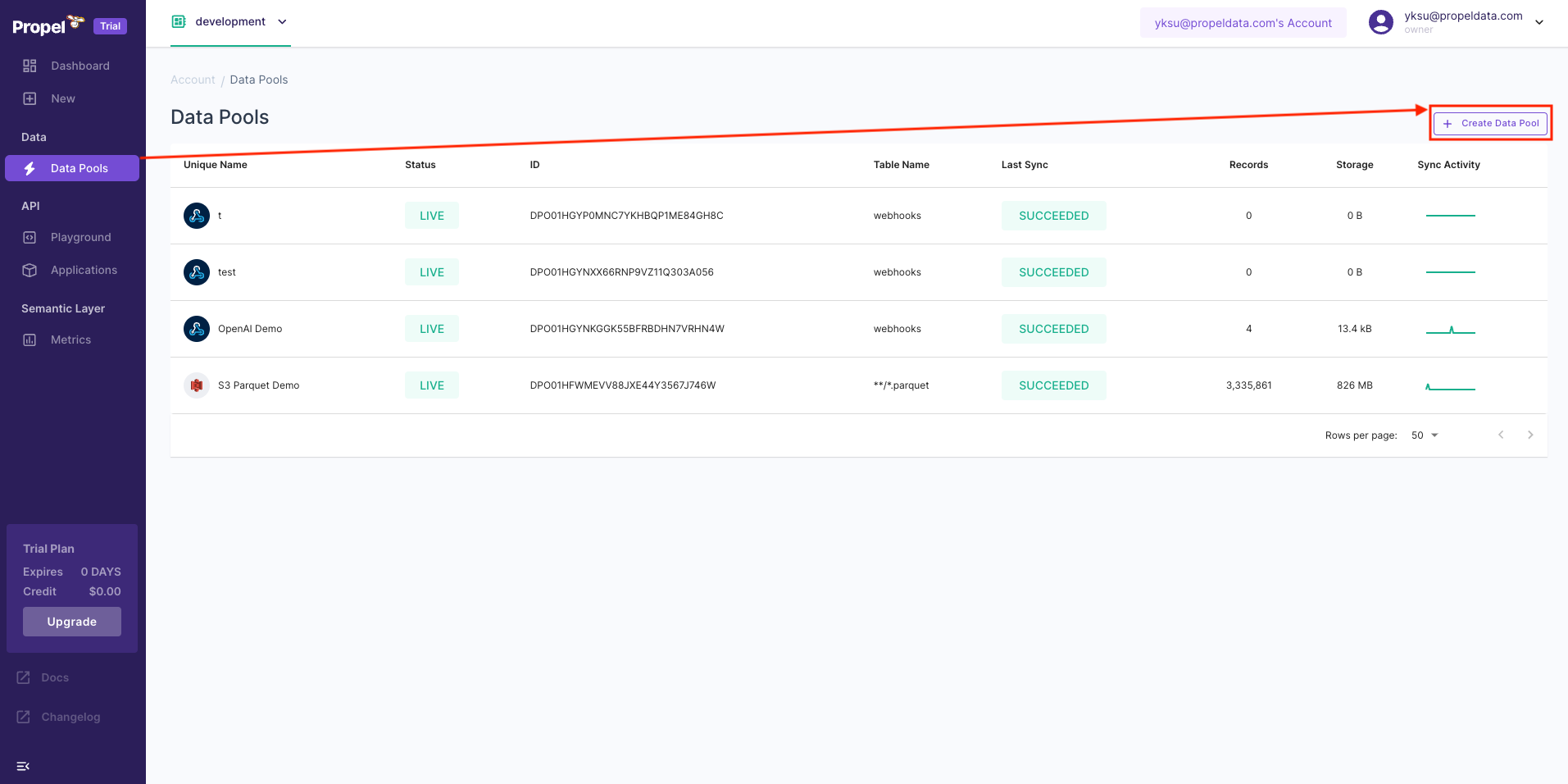 At Propel, we love tacos. So our sample data is taco-themed 🌮!You will see all data sources supported, as well as the “TacoSoft Demo Data”.
At Propel, we love tacos. So our sample data is taco-themed 🌮!You will see all data sources supported, as well as the “TacoSoft Demo Data”.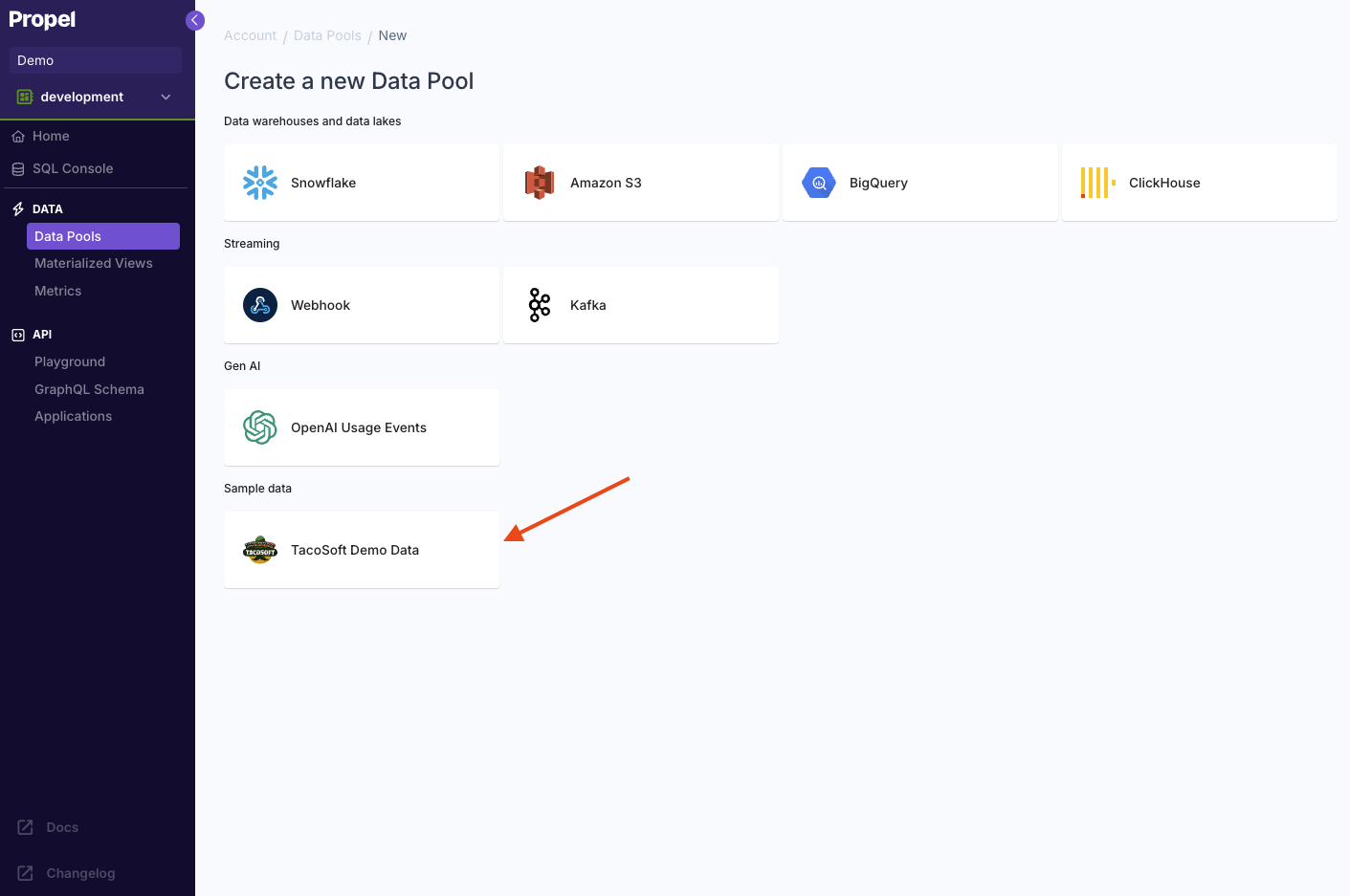 Select the “TacoSoft Demo Data”, then click “Create Data Pool”.
Select the “TacoSoft Demo Data”, then click “Create Data Pool”.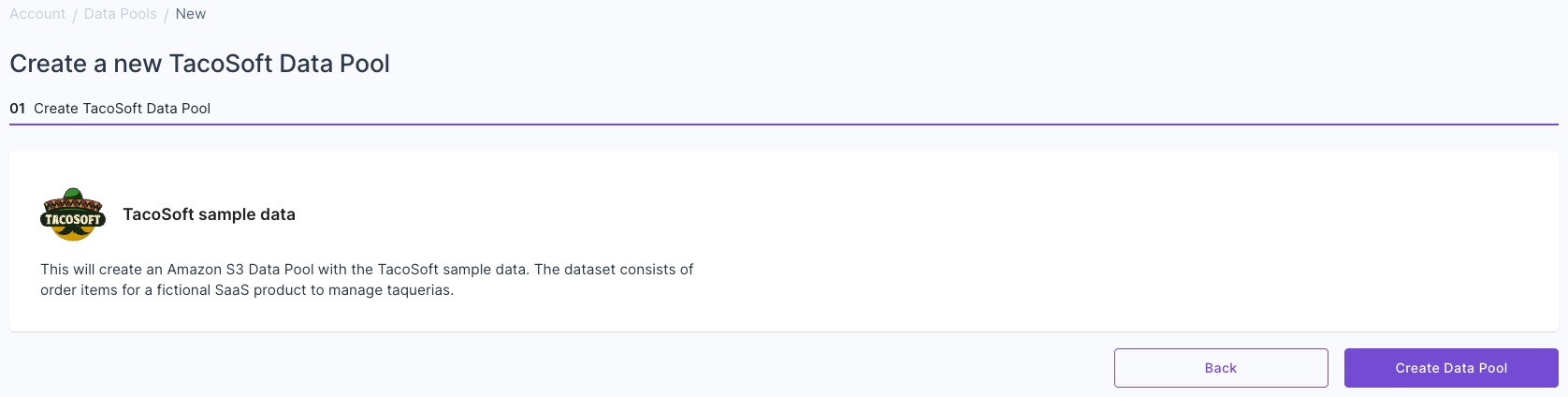 Once you create it, you will see the “TacoSoft Demo Data” Data Pool.
Once you create it, you will see the “TacoSoft Demo Data” Data Pool.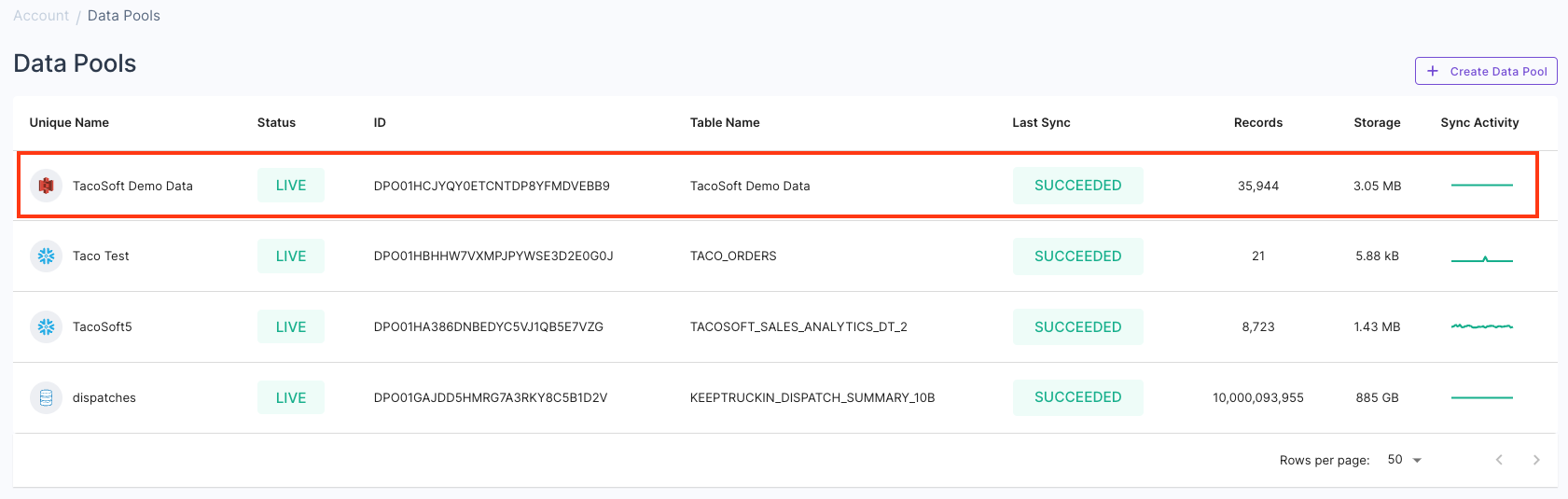 You can click on it and the Data Pool will start syncing.
You can click on it and the Data Pool will start syncing.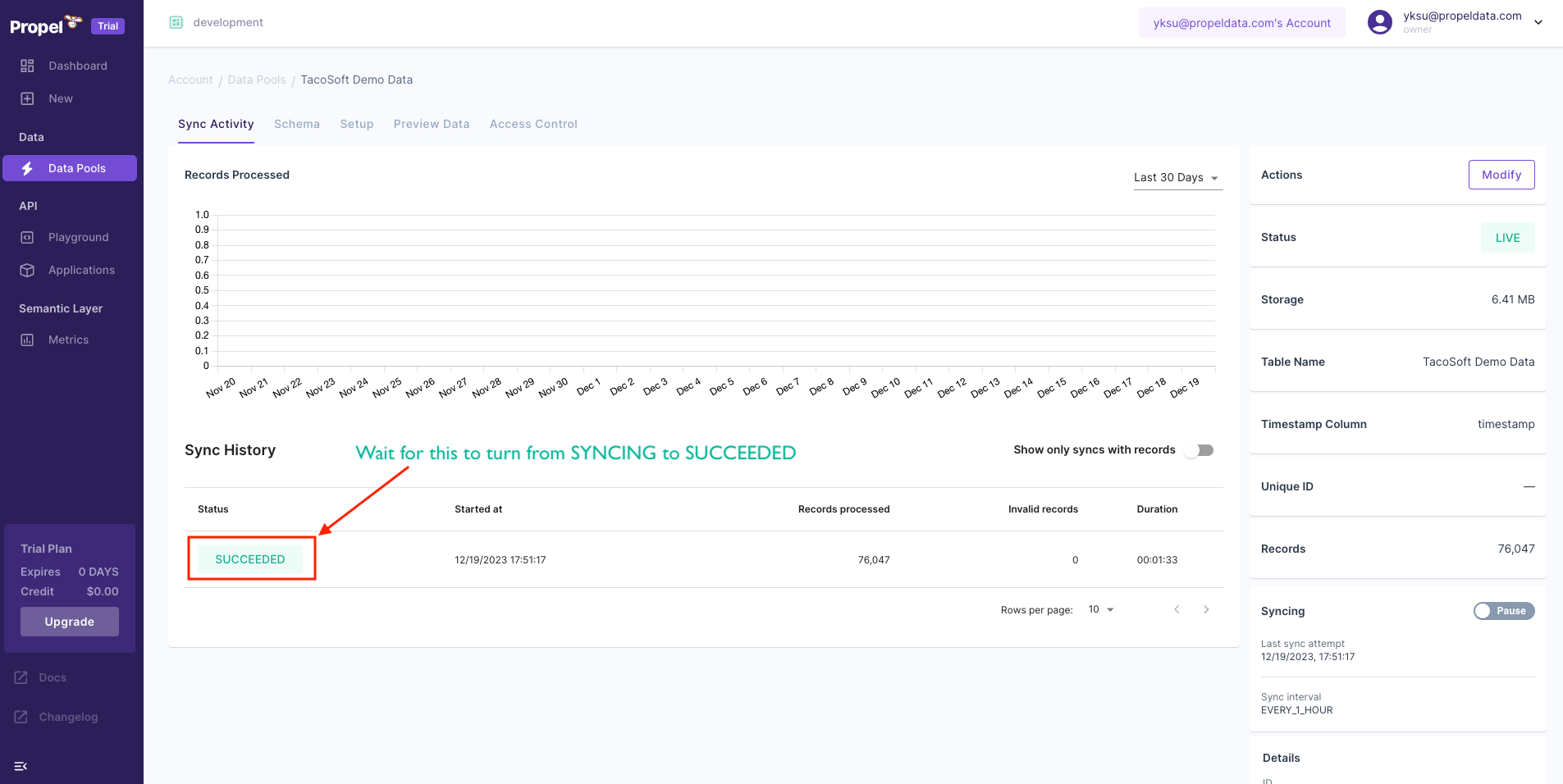 Once it’s finished, on the “Preview Data” tab, you can see the actual data.
Once it’s finished, on the “Preview Data” tab, you can see the actual data.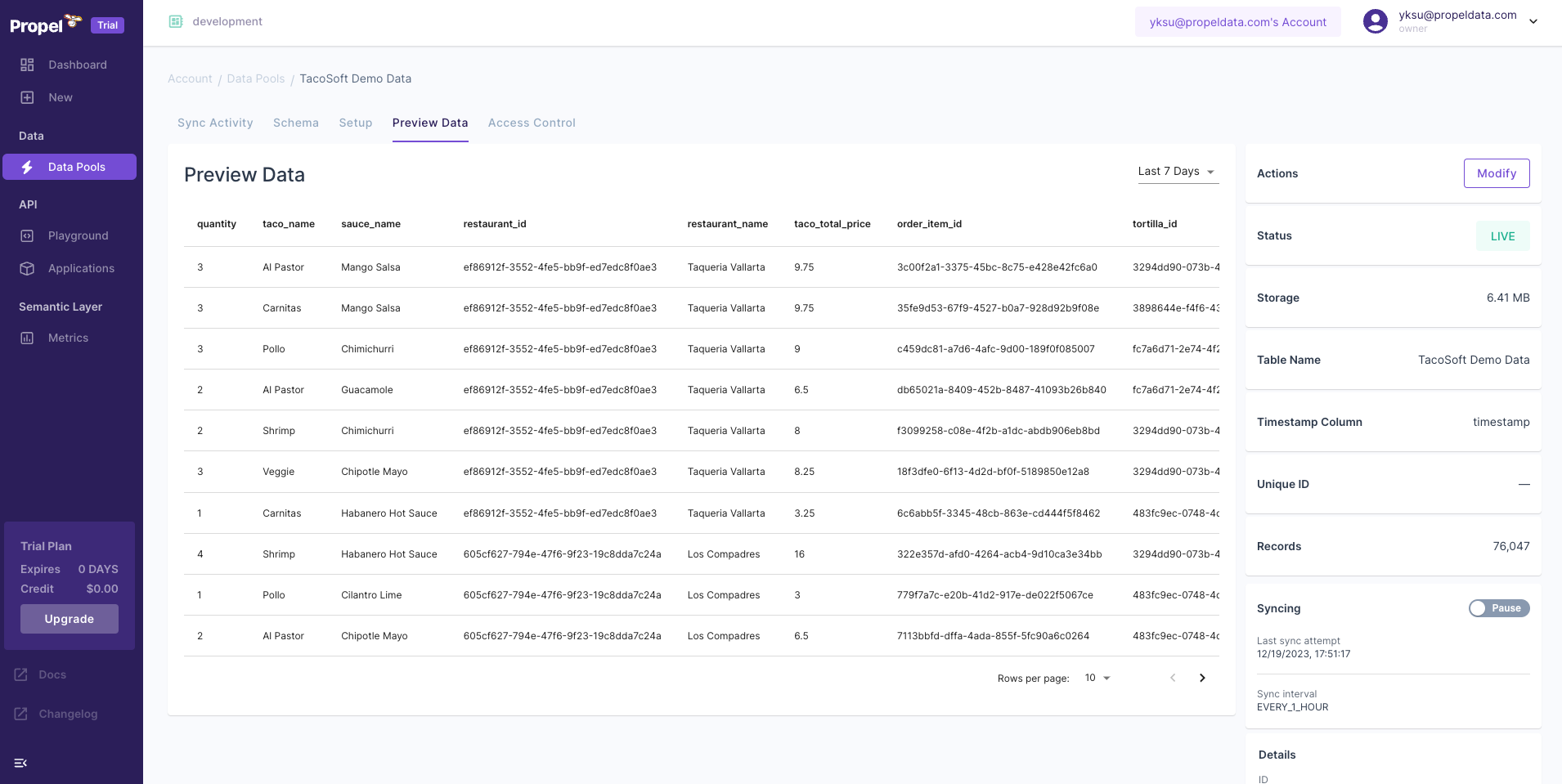






3
Query the data using SQL
Now that you have a Data Pool with data, let’s query it!Go to the “SQL Console” in the left-hand sidebar.And see the results!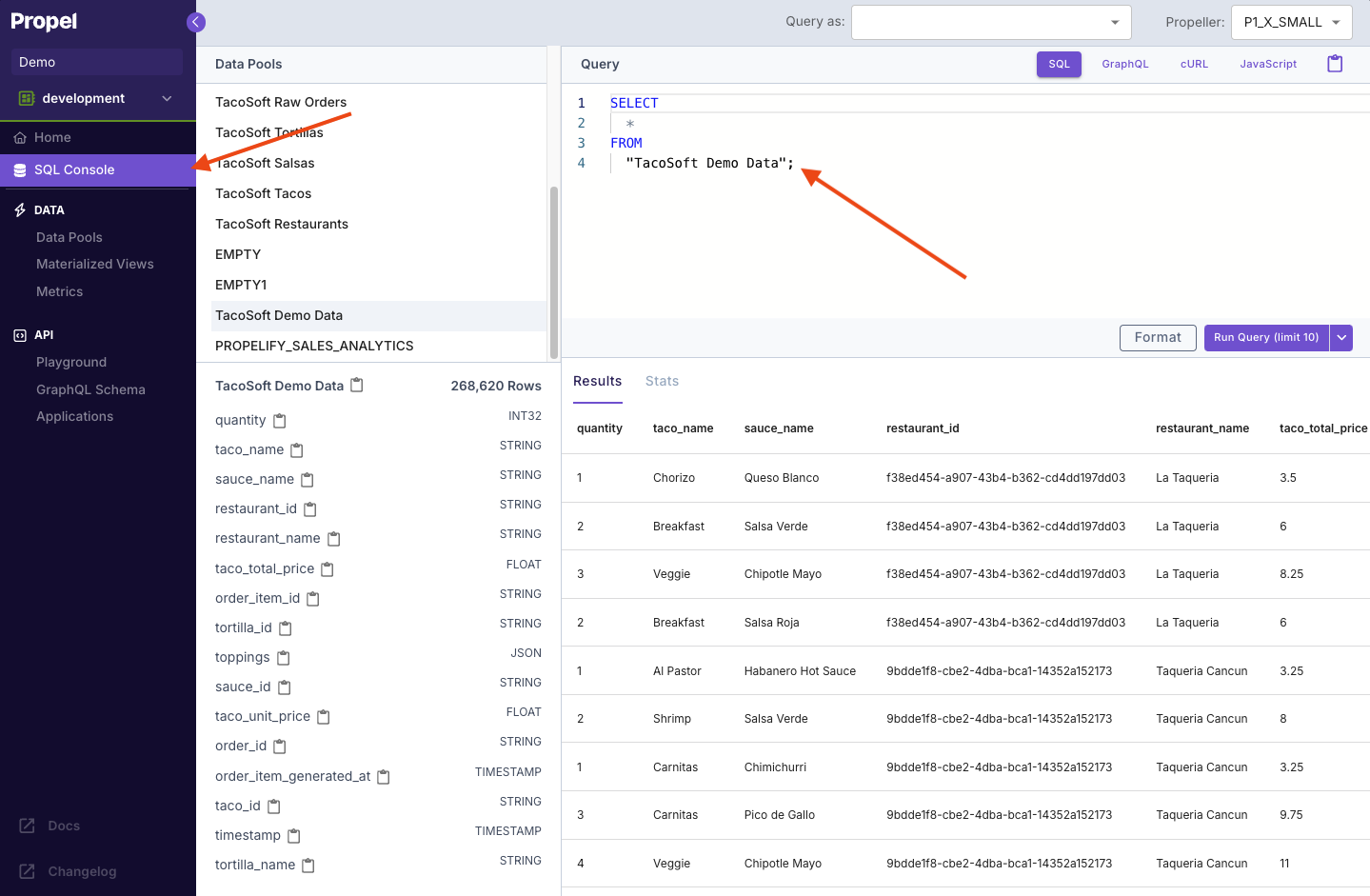

4
Query the data via the API
Now that you’ve queried the data via SQL, let’s query the data via the API.Under the “API” section, click on the “Playground” in the left-hand sidebar.The API Playground is a powerful tool for exploring your data and constructing queries. It provides an interactive interface on the left side for building queries, and displays the corresponding GraphQL API request on the right side.To create your first query, follow these steps: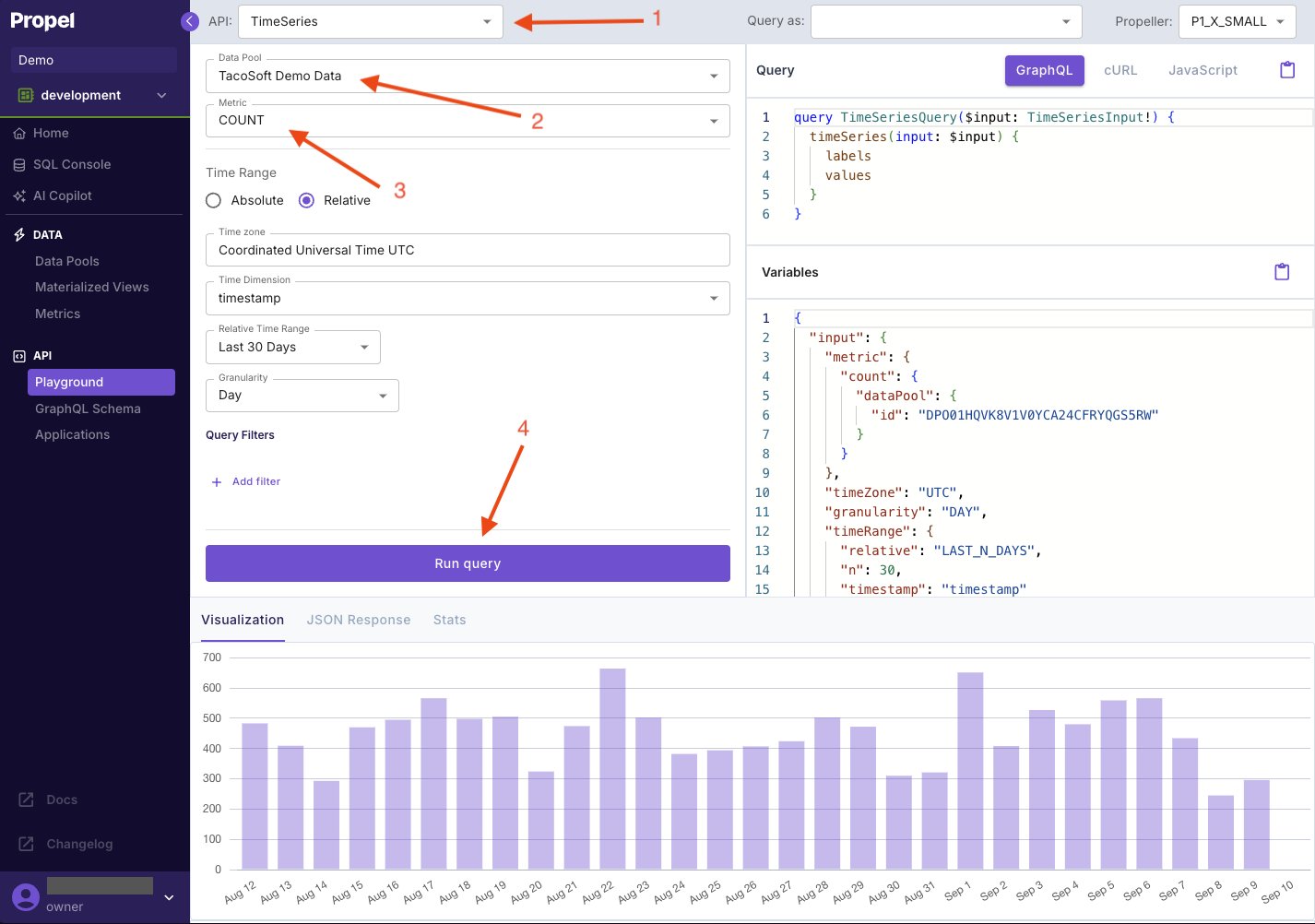 This query will return the total number of order items over time.🎉🍾🎈 You’ve made your first query!
This query will return the total number of order items over time.🎉🍾🎈 You’ve made your first query!
- API type: Choose the “Time Series” API from the dropdown menu.
- Data source: Select the “TacoSoft Demo Data” Data Pool.
- Metric: Pick the “COUNT” Metric to count the number of records.
- Execute: Click the “Run Query” button to execute your query.

5
Create a Propel Application and get the API credentials
Next, we’ll want to make queries from a Next.js application.To get your API credentials, you’ll need to create a Propel Application.Go to the “Applications” section and click “Create Application”. Enter the following information: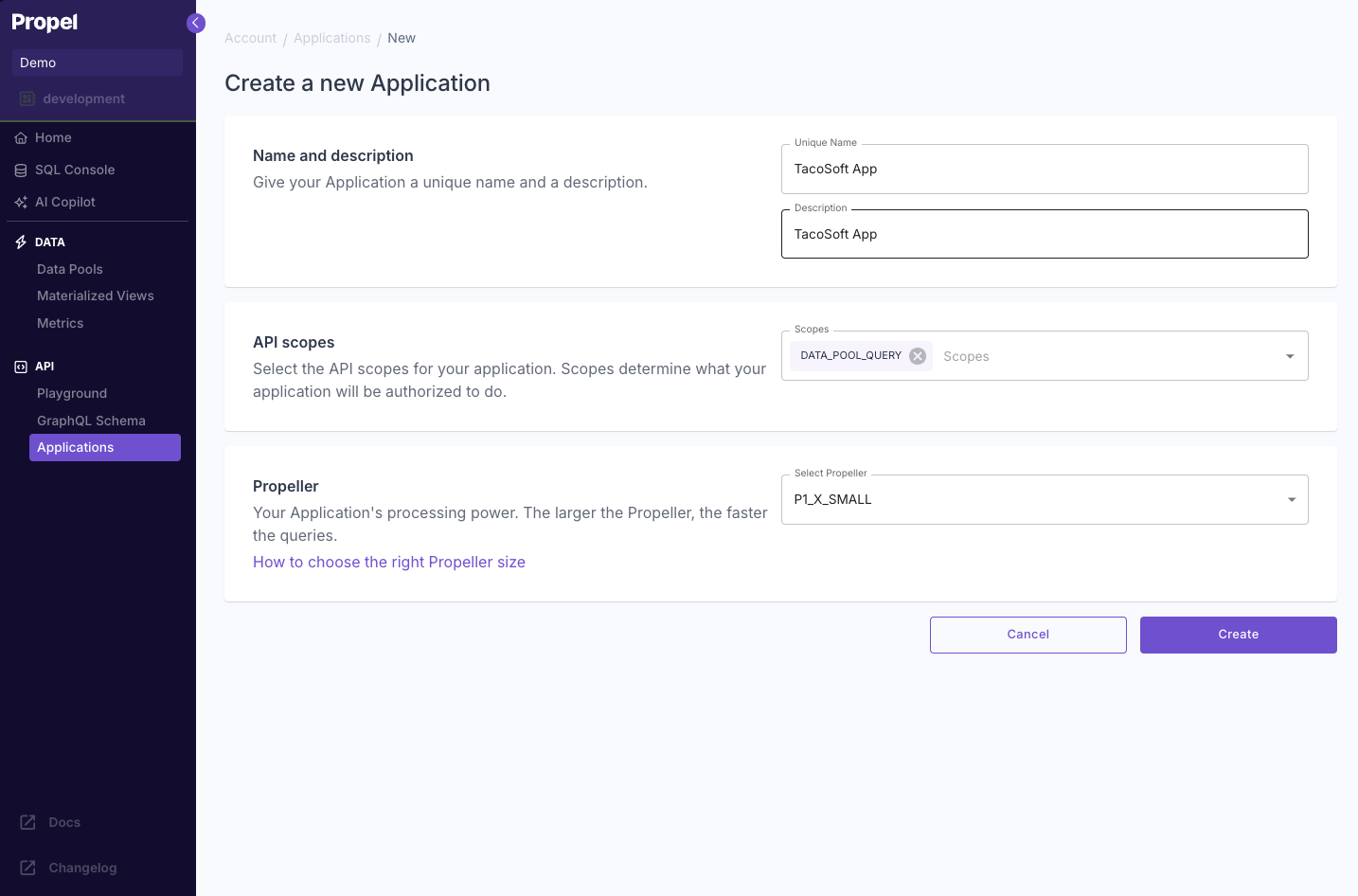
- Give your Application a unique name: “TacoSoft App”
- Give your Application a description: “TacoSoft App”
- For the API scopes, you’ll want your Propel Application to have the “DATA_POOL_QUERY” scope.
- The Propeller determines how fast the queries made with this Application are. For our Quickstart, you can select
P1_X1_SMALL. - Click “Create”

6
Run the Propel Next.js Starter App
The Propel Next.js Starter App is a project bootstrapped with create-next-app, integrated with Propel’s Embeddable UI Kit to create a sample dashboard.First, clone the repo for the Propel Next.js Starter App:orOnce you’ve cloned the repo, You’ll need to set your Propel Application’s client ID and secret in a Then, update the Install dependencies:Now you are good to run the app locally!Now, if you visit http://localhost:3000, you’ll see your app running.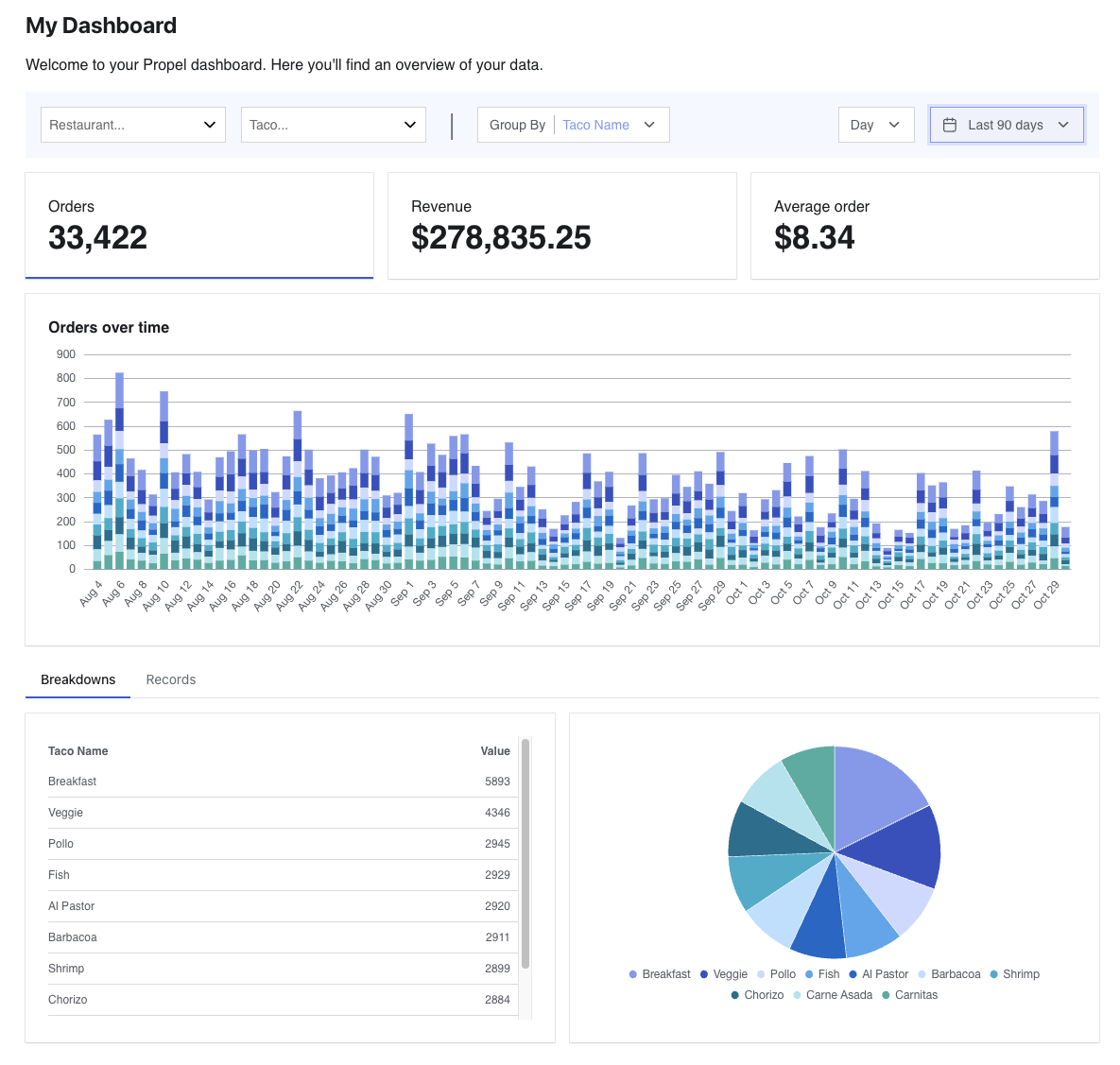 Now you have a working Next.js app serving data from Propel 🎉!
Now you have a working Next.js app serving data from Propel 🎉!
cd into its directory:.env.local file. To do this, first make a copy of the .env.sample included in the app’s root directory:.env.local file to include your Propel Application’s client ID and secret:

