- Flattens nested JSON into tabular form
- Flattens JSON array into individual rows
- Combines data from multiple source Data Pools through JOINs
- Calculates new derived columns from existing data
- Performs incremental aggregations
- Sorts rows with a different sorting key
- Filters out unnecessary data based on conditions
- De-duplicates rows
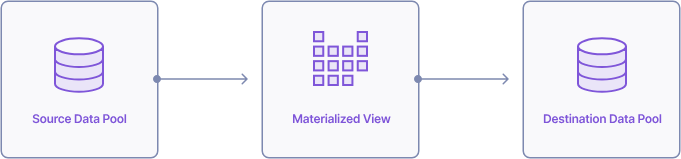
Illustration of data flowing from a source Data Pool, through a Materialized View, and into a destination Data Pool.
How do Materialized Views work?
Materialized Views in ClickHouse work by automatically executing a specified SQL query over new data inserted into a source Data Pool and writing the query results into a destination Data Pool. When creating a Materialized View, you define a SELECT query that transforms or aggregates data from one or more source Data Pools. You also define a destination Data Pool where the resulting data will be written.
Diagram of (1) an insert to a source Data Pool, (2) the insert triggering a Materialized View, (3) the Materialized View executing its SQL query on the newly inserted data, and (4) the Materialized View's query results being written to the destination Data Pool.
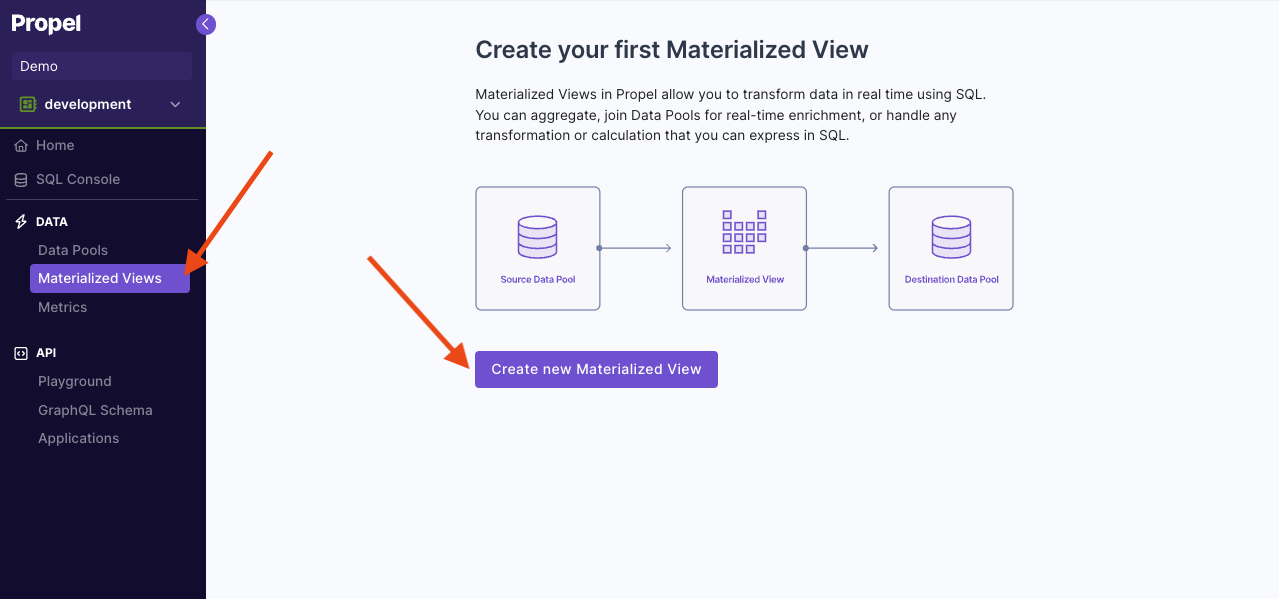
Creating a Materialized View
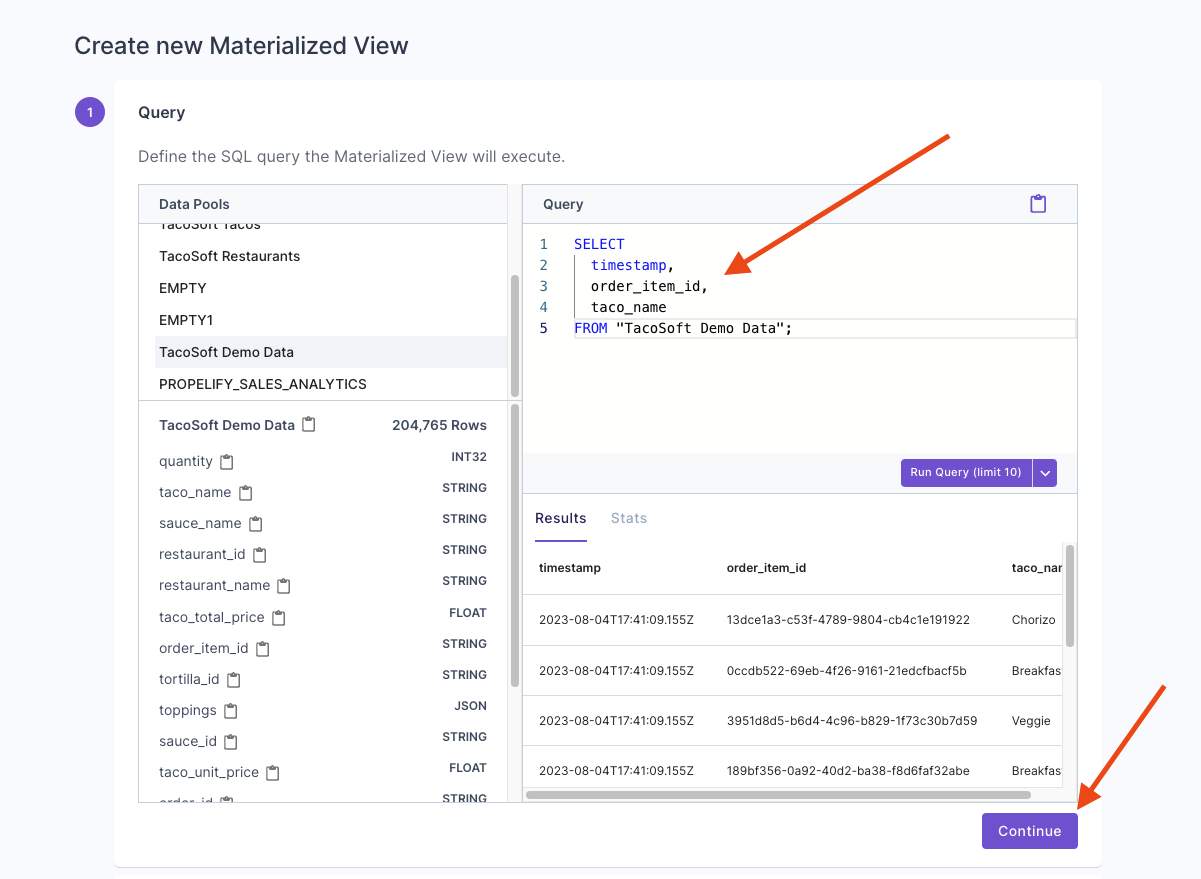
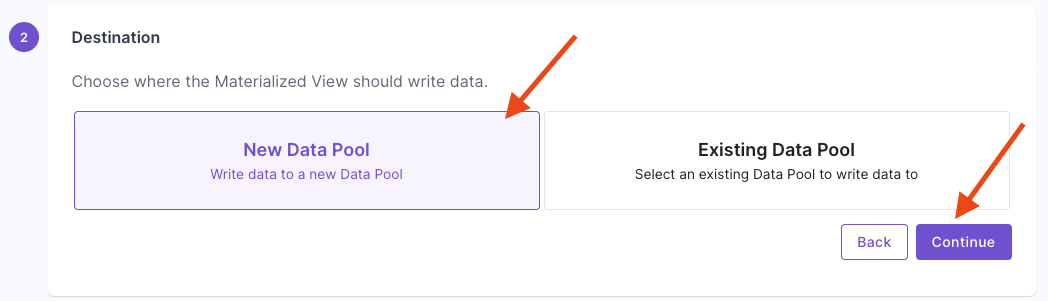
This section provides step-by-step instructions on creating a Materialized View in the Console, the API, and Terraform.- Console
- API
- Terraform
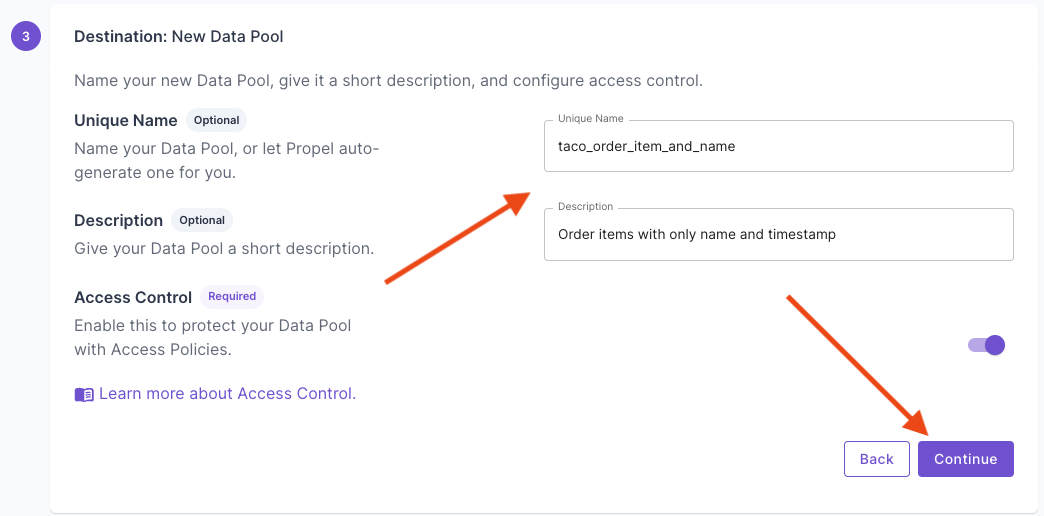
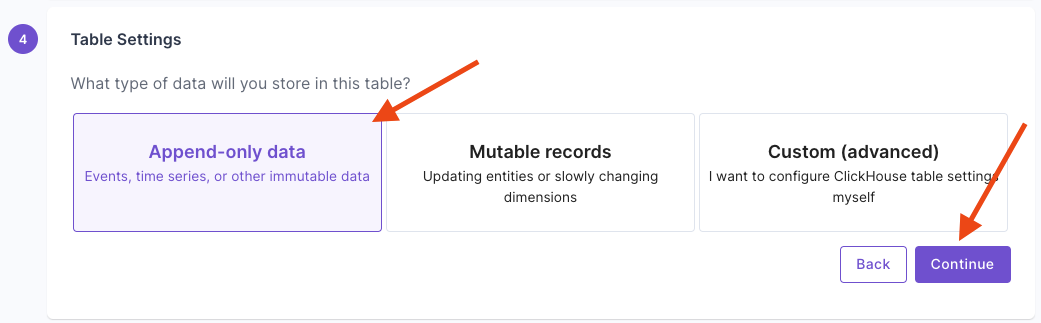
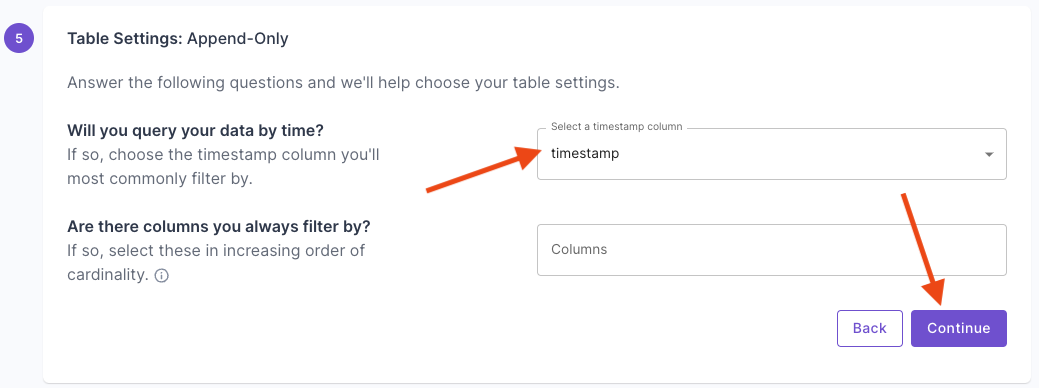
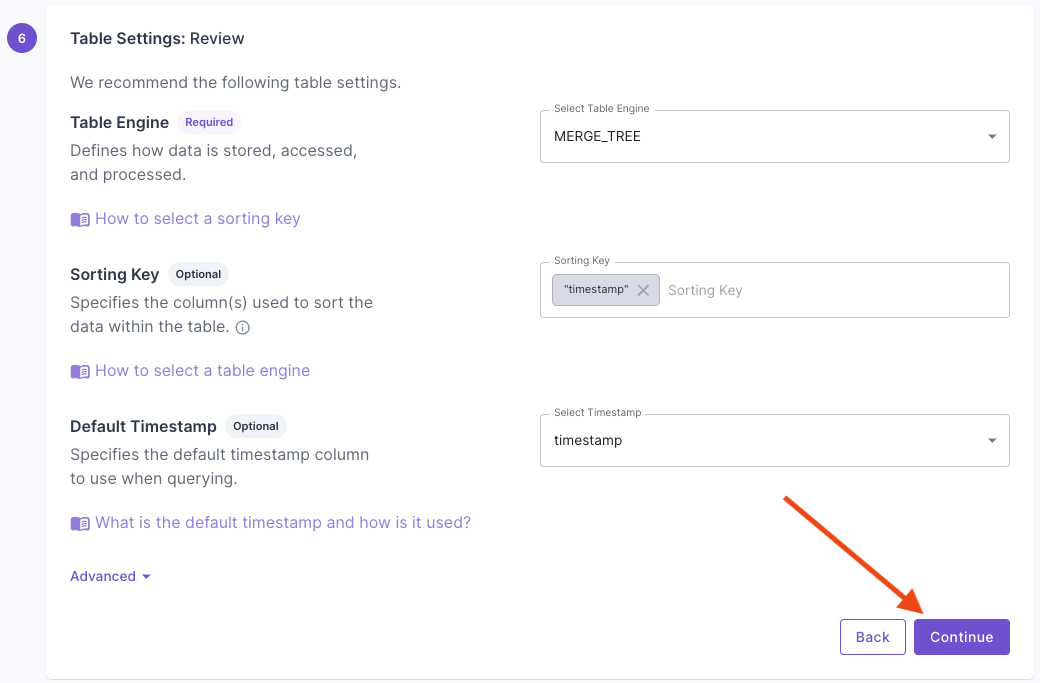
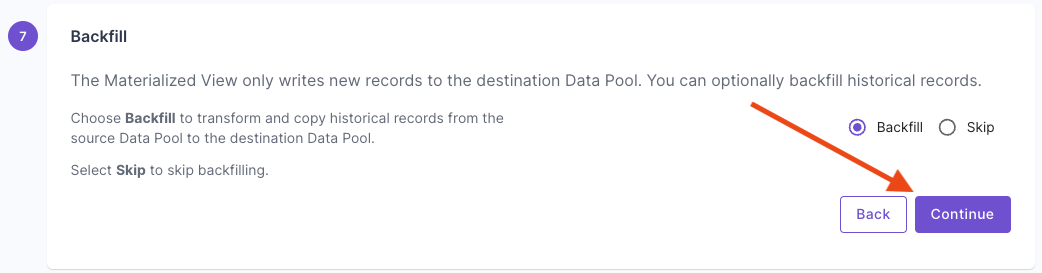
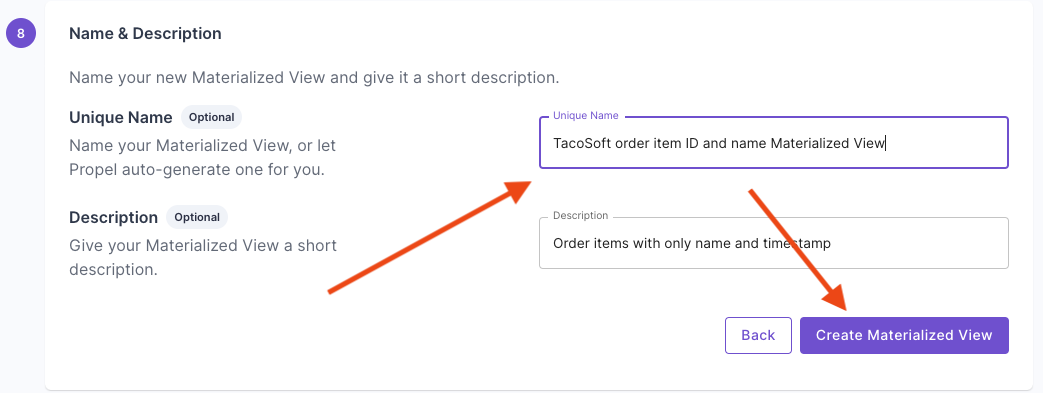
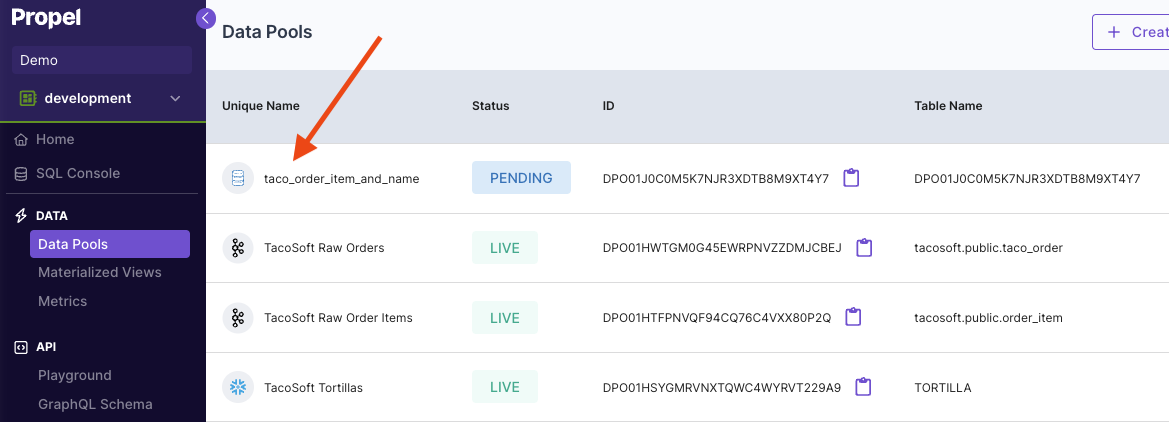
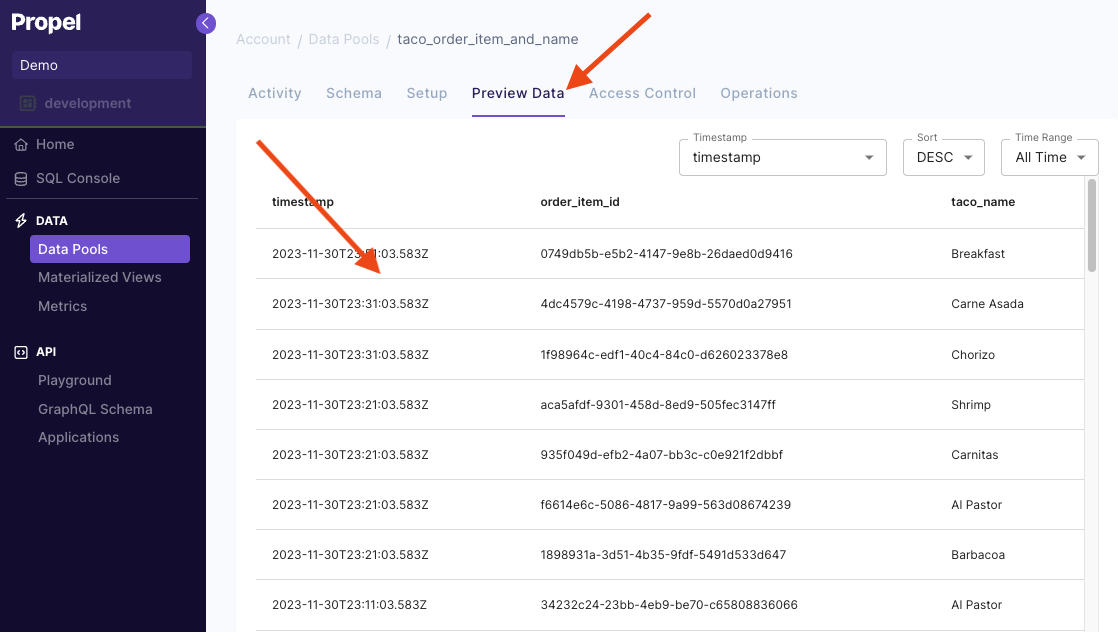
Materialized View examples
In this section, we will provide examples of common use cases solved with Materialized Views. For all the examples, we’ll use a source Data Pool calledevents with two columns:
_propel_received_at(TIMESTAMP)_propel_payload(JSON)
_propel_received_at and _propel_payload columns. Then click on the Data Pool, click on “Schema” tab and paste the event below to create sample records.
The JSON events in the _propel_payload column are of the form:
Example 1: Flatten nested JSON into tabular form
The following Materialized View flattens the JSON into individual columns. In Propel, you can access nested JSON keys by using dot notation, as shown in the example below. We are also using theparseDateTimeBestEffort function to parse the timestamp from a string to ClickHouse timestamp.
- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | MergeTree |
| Sorting Key | created_at |
Example 2: Flatten JSON array into individual rows
The following Materialized View flattens a JSON array into rows. Given a tableTacoOrders with the following schema:
- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | MergeTree |
| Sorting Key | orderDate |
Example 3: Combines data from multiple source tables through JOINs
Given an additional tablestores with two columns,
- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | MergeTree |
| Sorting Key | created_at |
Example 4: Calculates new derived columns from existing data
This Materialized View calculates the total price multiplying thetaco_count times the price column.
- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | MergeTree |
| Sorting Key | created_at |
Example 5: Perform incremental aggregations
The Materialized View below incrementally aggregates the number of tacos sold and sales bycustomer_id and month. This Materialized View uses the SummingMergeTree table engine to incrementally aggregate rows as they are written. To learn more, read our guide on How to select a table engine and sorting key.
- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | SummingMergeTree |
| Sorting Key | month |
Example 6: Sorts rows with a different sorting key
The Materialized View below creates a destination Data Pool with a different sorting key. It sorts the rows by thecheckout_time column instead of the _propel_received_at column of the source Data Pool.
- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | MergeTree |
| Sorting Key | checkout_time |
Example 7: Filters out unnecessary data based on conditions
The Materialized View below filters out rows older than 2024.- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | MergeTree |
| Sorting Key | created_at |
Example 8: Deduplicating rows
The Materialized View below flattens and deduplicates events. It uses the ReplacingMergeTree table engine to duplicate events with the same sorting key. To learn more, read our guide on How to select a table engine and sorting key.- SQL
- API
- Terraform
| Destination Data Pool | |
|---|---|
| Table Engine | ReplacingMergeTree |
| Sorting Key | created_at, order_ids |
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between materialized views and views?
What is the difference between materialized views and views?
Do Materialized Views transform data in real-time or on a schedule?
Do Materialized Views transform data in real-time or on a schedule?
How much do Materialized Views cost?
How much do Materialized Views cost?
What happens if I delete a Materialized View?
What happens if I delete a Materialized View?
Can a Materialized View be modified?
Can a Materialized View be modified?
What happens if I update or delete data in the source Data Pool with the update or delete API?
What happens if I update or delete data in the source Data Pool with the update or delete API?

